Exchange 2013 and 2016 configuration
This guide shows the steps necessary to configure a newly installed Exchange 2013 or 2016 server for receiving email from POPcon or POPcon PRO (or from the internet directly) and for sending out emails to the internet.
Basically you need to perform these simple steps:
- Add your own internet domain to the “Accepted Domains” list
- Configure a Send Connector for outgoing emails
- Configure the Default Frontend Receive Connector for incoming emails (from POPcon) without Authentication
- Assign email addresses to users
- Install and configure POPcon to download POP3 emails
1. Add your own internet domain to the “Accepted Domains” list
In contrast with previous versions of Exchange (2010, 2007, 2003), there is no longer the MMC application to manage the server. Everything is done with the new Exchange Control Panel (ECP) and the Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
Open the Internet browser and go to the following address: https://exchange.your-domain/ecp
It will redirect us to the login screen in order to authenticate before accessing the ECP.
Once you have entered your credentials, the ECP window appears:
As we've already mentioned, all of the management operations happen here. The first step to configure our server is to add our Internet domain to the "Accepted Domains" list. To do so, go to the Mail Flow option (on the left pane) and select “Accepted Domains” in the menu bar above. There should be a default setting, usually the internal domain name (here servolutions.dom) that you can leave as it is. Now, add a new accepted domain by clicking on the "+" icon:
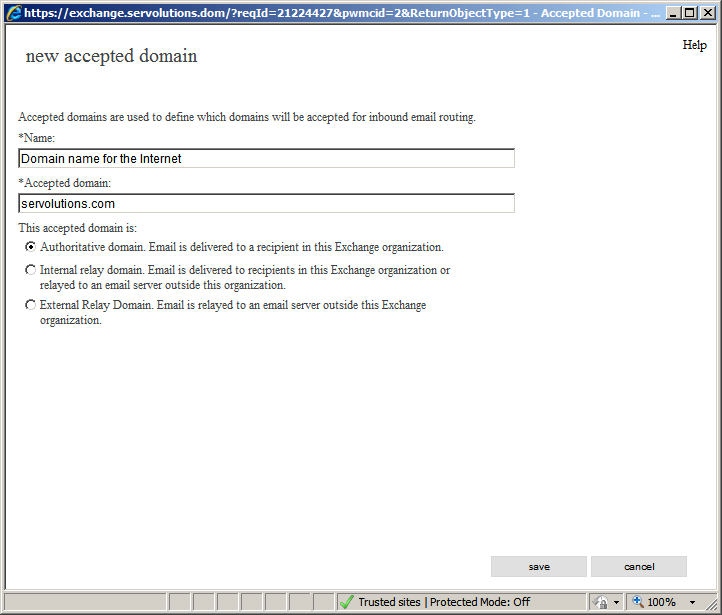
Now, a pop-up window opens. Add the Internet domain that we want our server to accept. In the "Name" field enter a descriptive name for our rule (In this case, "Domain name for the Internet" is the name that I've chosen). In the Accepted domain field enter the name of your Internet domain name (in this case, servolutions.com). Mark the "Authoritative domain" option and once done, click the SAVE button in the lower part of the window.
This setting indicates that this Exchange server will accept e-mails directed to the "servolutions.com" domain. The Authoritative domain option is to indicate that this server will be the one that processes all of the e-mails sent to the servolutions.com domain.
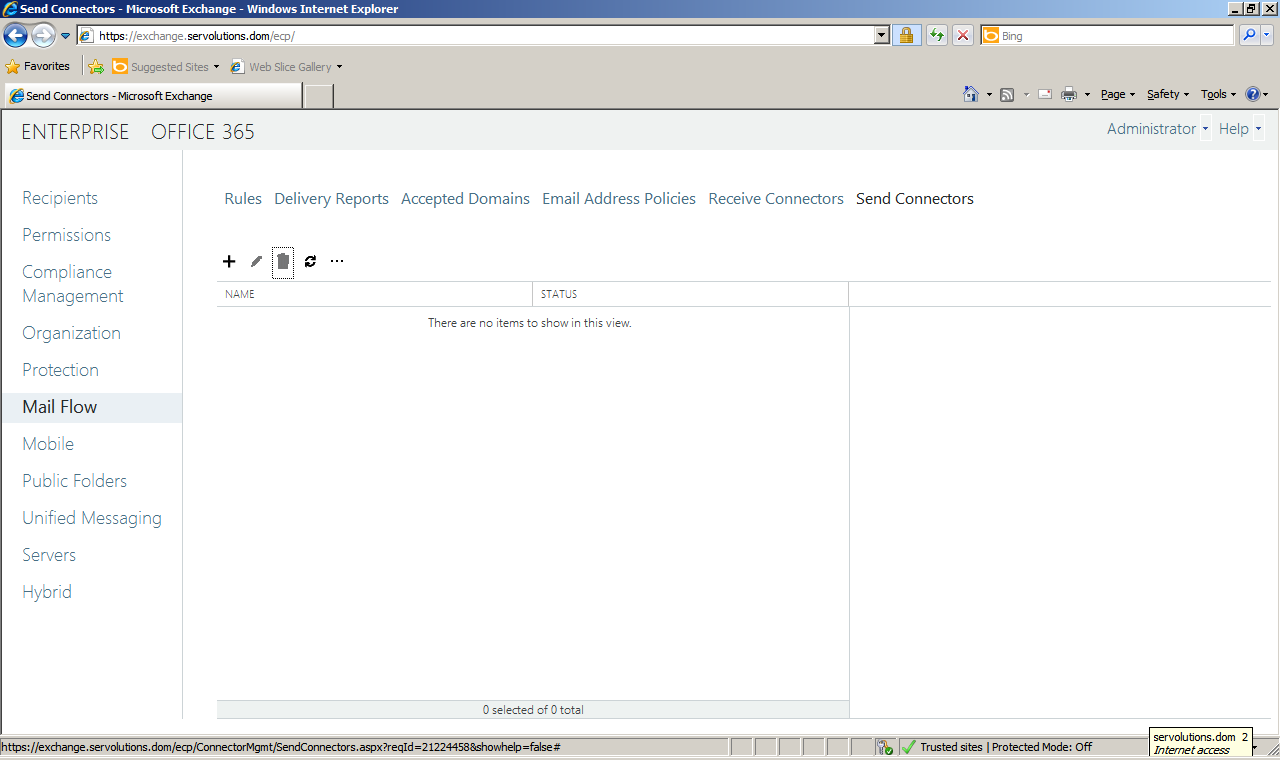
2. Configure a send connector for outgoing emails
The send connector is used to pipe outgoing emails from Exchange via your providers SMTP relay server to the internet.
In Exchange 2013 the “Hub Transport” role that existed in Exchange 2010 and 2007, is now integrated to the Mailbox server role. So now, all you have to do is click on the Send Connectors menu option.
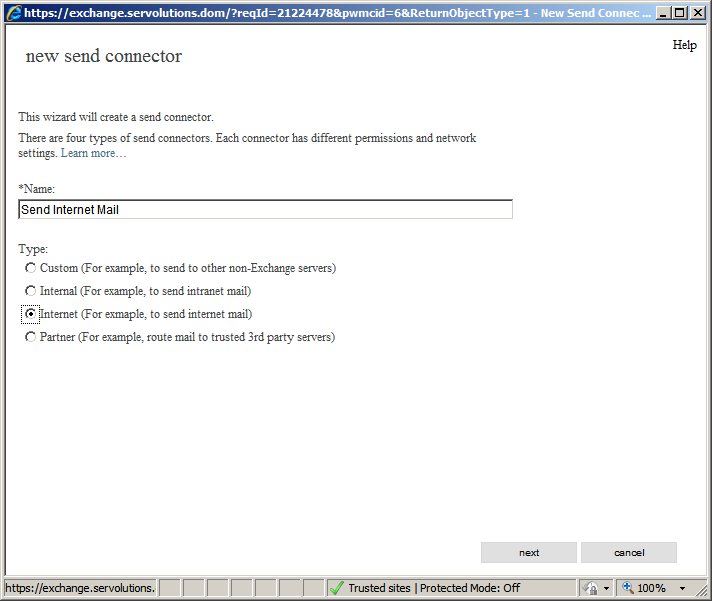
Here, we add a new send connector by clicking on the "+" icon. A new window will open. In the "Name" field enter a descriptive name for the connector (I've named it "Send Internet Mail"), select the Internet option and click in next.
In most cases your Exchange server will be on a normal internet connection with a dynamic IP address and you should use the webspace provider's SMTP relay server to send out internet through. This ensures our emails are not flagged as spam by the receiving end since it originate from a public IP address.
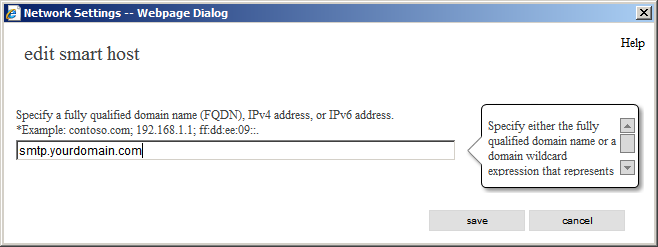
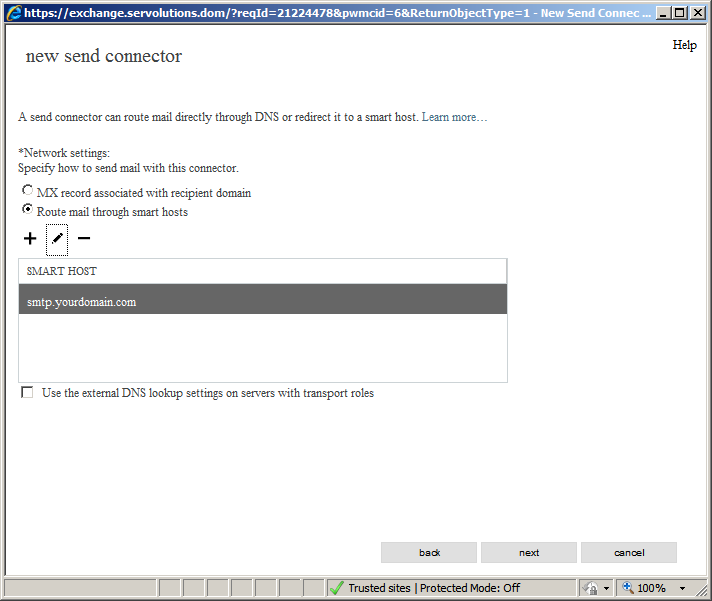
So in Exchange terms we will use a relay “Smart host” to send e-mail. For this option please select "Route mail through smart hosts" and in the next field add the smart host's address (FQDN).
Once finished, click on Save. The configuration will look like the image shown below.
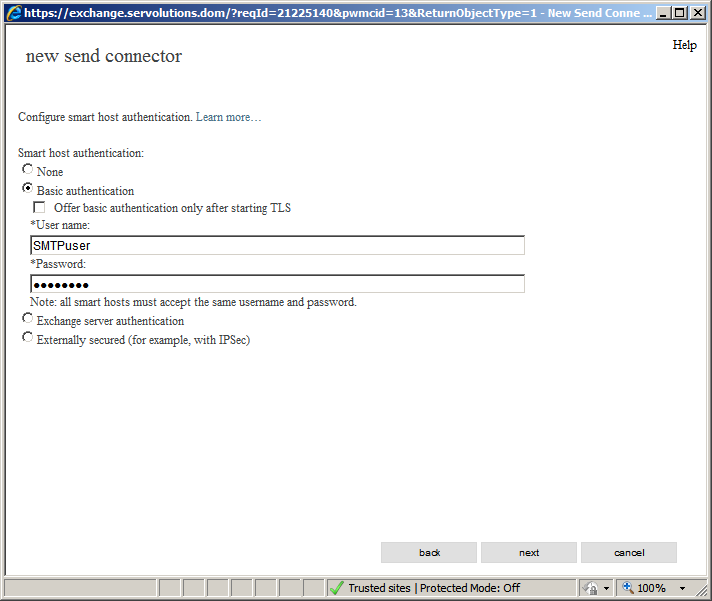
Click Next. In the next window we will enter the authentication data for the SMTP relay server / smart host. Every commercial relay server requires authentication to keep spammers from abusing them. Choose "Basic authentication" and enter your provider's SMTP server username and password. Note that if you have multiple logins for the server it is not important which one you use. It will not affect the email sender name, this log in is purely used to allow you to send email through the relay server.
Click on the Next button.
The next screen asks for the send connector e-mail routing rules. Here we can instruct our Exchange server to use a different e-mail server (smart host) to send e-mails depending on the domain we send to. This is seldom useful and does not allow different smart hosts depending on the sender domain. If you want that please check out our MultiSendcon, the multi-domain send connector for Exchange
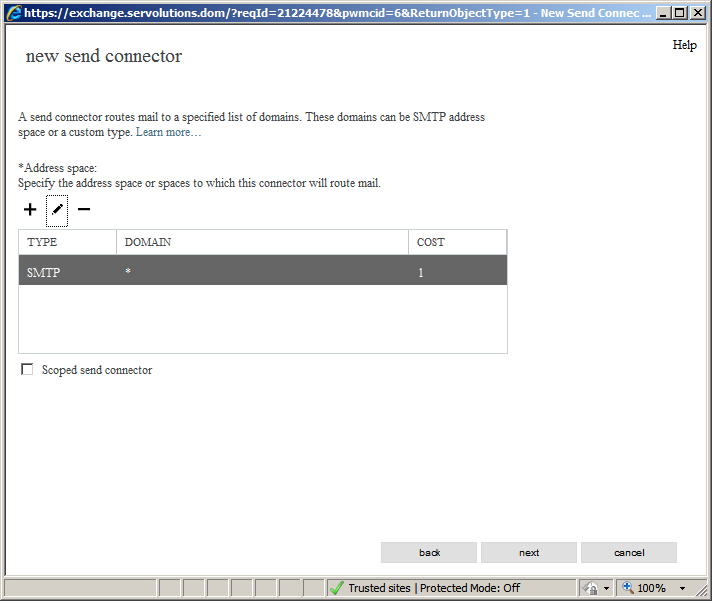
In our case only one server is required, so in the next screen we should put an asterisk "*" in the "Domain" field. The asterisk means that e-mail to any other domain outside our organization will be routed through this external smart host. Click on the Next button.
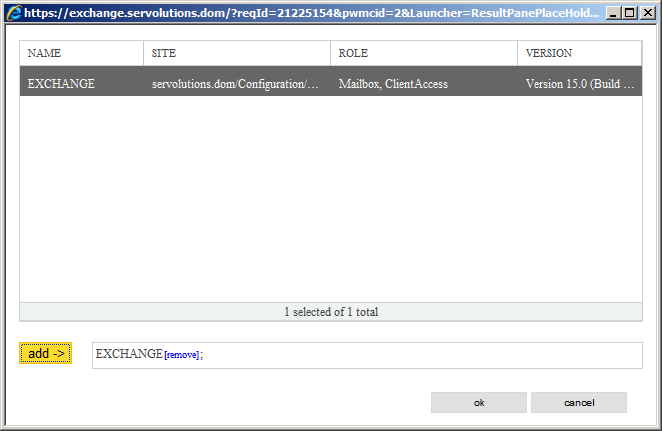
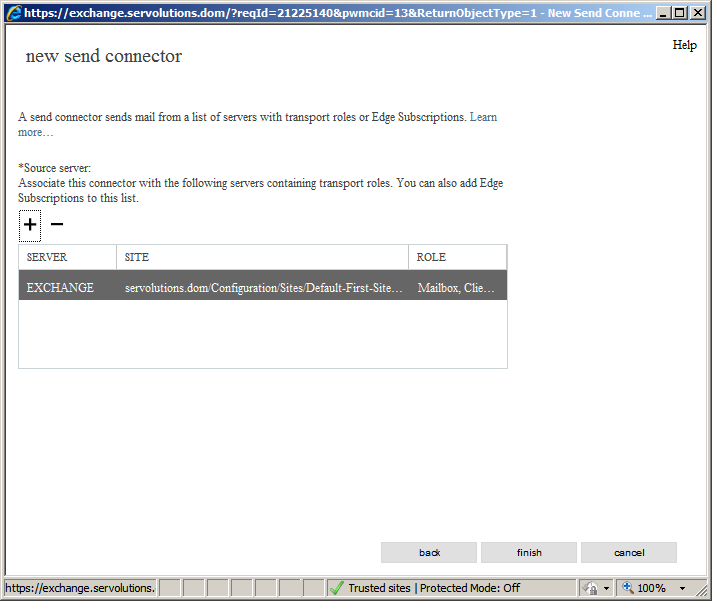
Another window will appear. In this screen we can indicate in which Exchange server this rule will apply. In this case, it applies to our one Exchange server. To set this rule, click on the “+” button and the next window (below) will appear. Here we select the server that this rule will apply. As we have one Exchange server only, we select it here and then click on the "add->" button, so it should look like this:
Once finished just click on the OK button and it'll return to the previous window with the changes made.
Once we are satisfied with the changes, click on finish.
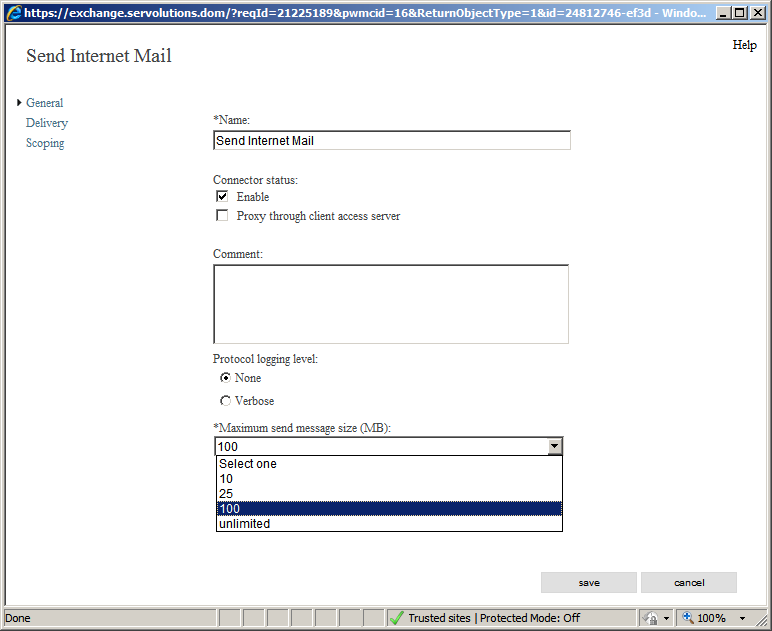
And now we're finished with our outgoing e-mail rule. But one more change should be applied to make it complete: The maximum outgoing message size is set to 10MB by default. This is how to change it: Please click the pencil icon to review and edit our changes:
Change the maximum message size for outgoing emails to a value that is more convenient here and save the changes clicking on the Save button.
With this done, we’re finished with the outgoing mail configuration. Now we’re ready to take a look at the e-mail receiving configuration.
3. Configure the "Default Frontend" receive connector for incoming email
POPcon uses SMTP to forward emails to Exchange. For this to work we need to have a Receive Connector configured on the Exchange 2013 side and make sure the configuration settings of the new receive connector are correct, especially the maximum email size (which is set to 10MB by default and can cause many problems) and we need to add the anonymous user to the permission group in order to allow POPcon to transfer email into the Exchange server.
Important: You also need to make sure to not install the Windows "Simple Mail Transfer Protocol" service. This service could block the Exchange SMTP transport from actually answering the SMTP IP port (25) and could cause Emails to loop back to the internet if installed. Check Administrative tools, Services and disable this service in case it is installed.
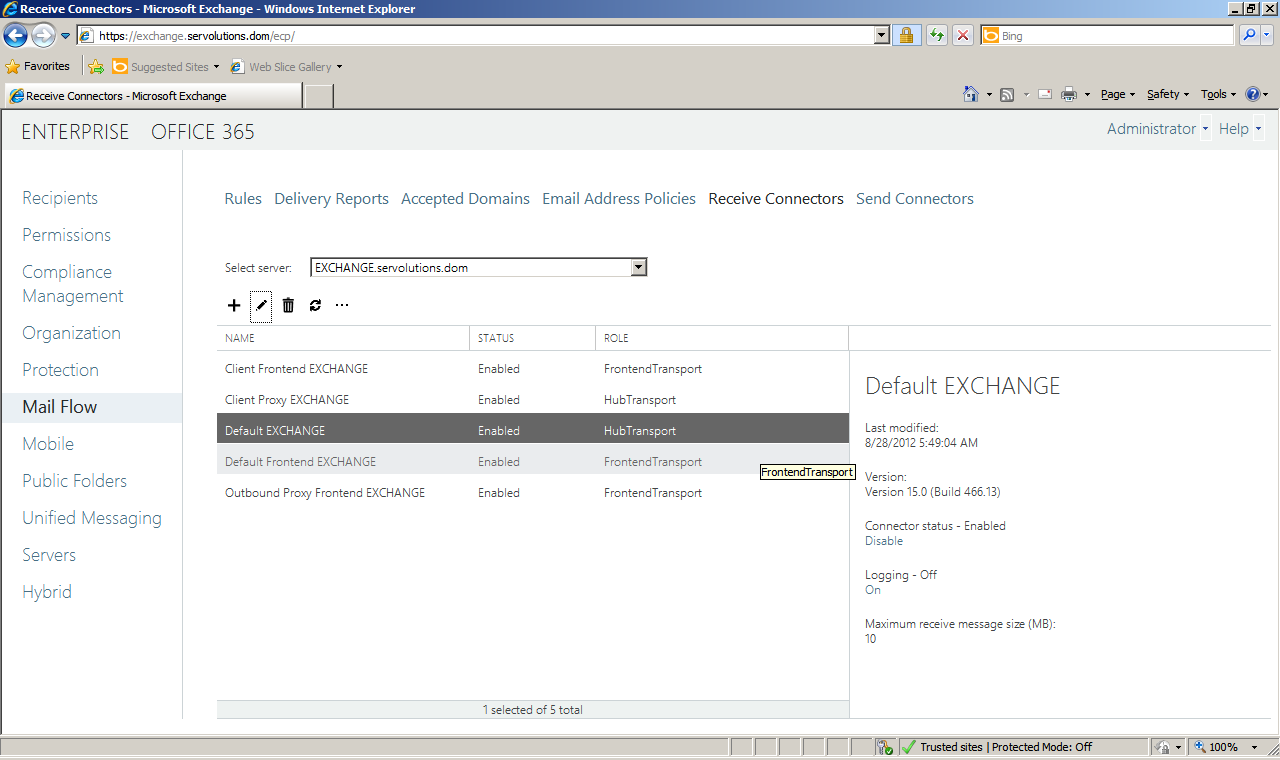
Back to the Exchange configuration: In order to configure the incoming mail rules, open the Exchange Control Panel, go to the "Mail Flow" option located on the left pane and in the right pane, click on "Receive Connectors". The screen will look like the one pictured below.
Select the "Default Frontend" connector and click the pencil icon to change the settings.
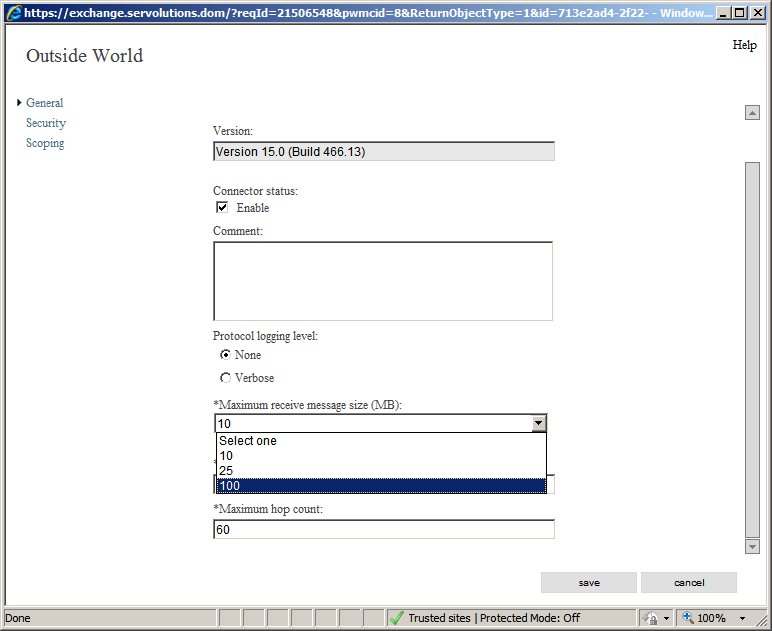
In the General option we need to change the "“Maximum receive message size" from the default 10MB to 100MB, so larger E-Mails don't get stuck between POPcon and the Exchange Server. If you want you can later limit the maximum message size in the Exchange general options or even for an individual user in their mailbox options and cause Exchange to return undeliverable messages if the email is too large. Check the image below:
Once finished, click on the save button.
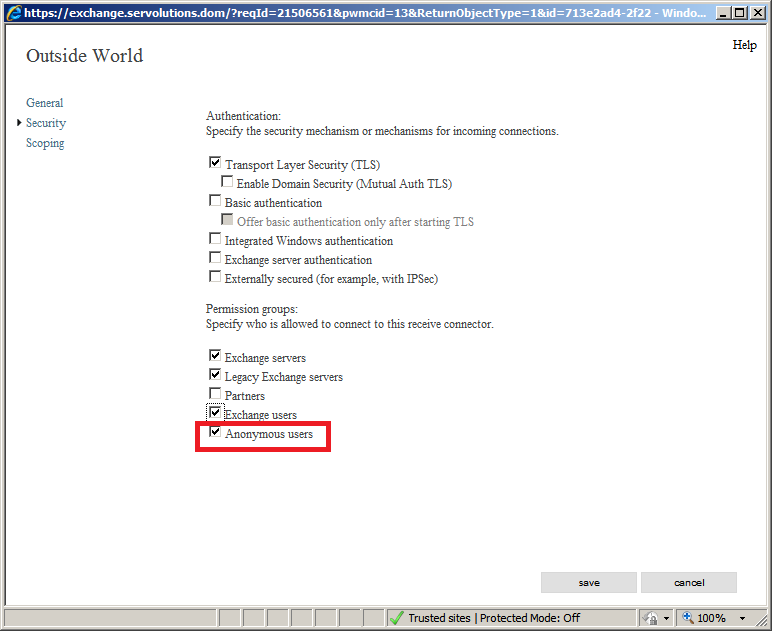
Now go to the Security option. Make sure to mark the checkbox which says "Anonymous users" (inside the red square in the image below). Anonymous users are all email senders from outside your organiation, so this check mark allows email senders from outside to deliver email into Exchange. Check the "Anonymous users" checkbox and click on the save button.
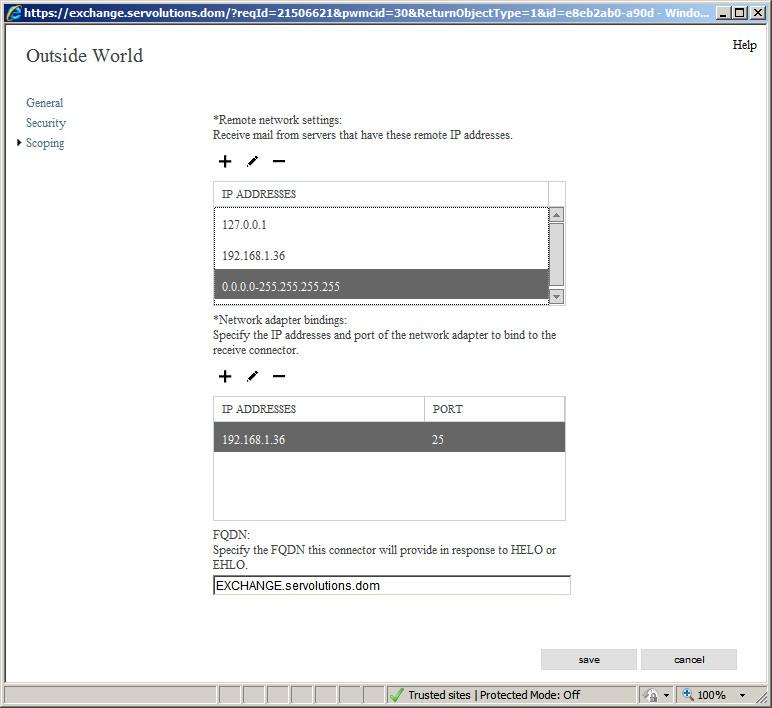
Now, go to the Scoping option. Make sure to the Exchange server's real IP address, like in the image below. Also make sure that the "Network adapter bindings" option shows the server's IP address or "All available IPv4" and port 25. You can change the FQDN field to reflect the mail server’s fully qualified hostname or you can leave it as it is. That option is not important for POPcon. Click on the save button. With that, we're finished setting up our receive connector.
4. Assign email addresses to users
All you need to do now is to add SMTP email addresses to users in the active directory. Users can have more than one SMTP address, for example they can have info@yourcompany.com in addition to jeff.smith@yourcompany.com.
Exchange provides the convenient E-Mail Address Policies feature that allows you to assign identically formatted email addresses to all (including future) users.
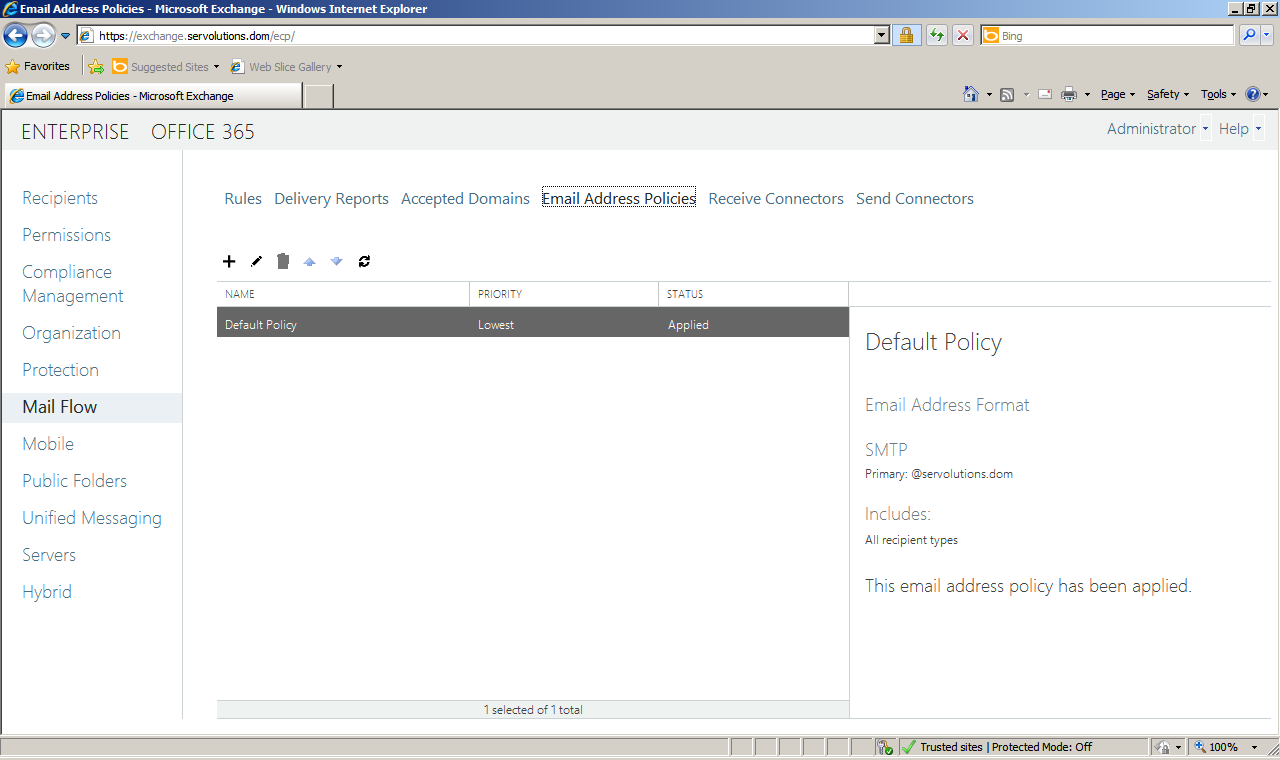
We edit the default email address policy like this: Open the Exchange Control Panel and select the Mail Flow option on the left pane, then select Email Address Policies menu option on the right pane. Select the default policy and click on the edit/pencil icon.
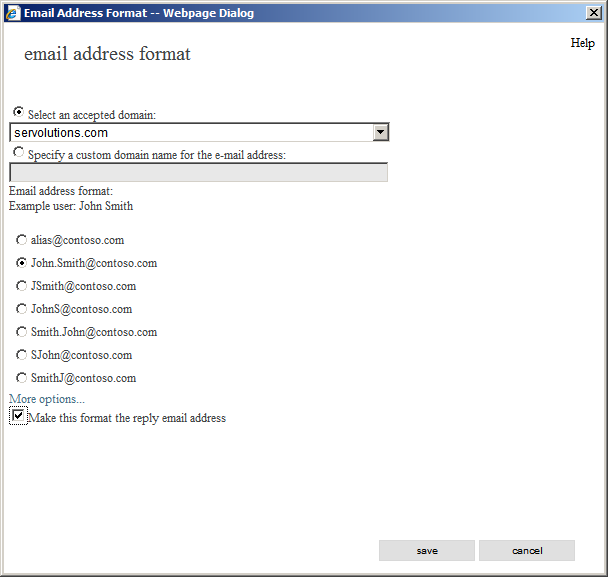
This opens the E-mail address format window. Go straight to "Email Adress Format" and click in the edit button (again, the pencil icon). Select the domain in which we want to apply the new rule (in this example, servolutions.com) and below we can select the format that we will use for all of our e-mail addresses (in this case John.Smith@servolutions.com). Finally, we mark the checkbox named "Make this format the reply email address" in order to force users to use this naming rule. Once finished, click on Save.
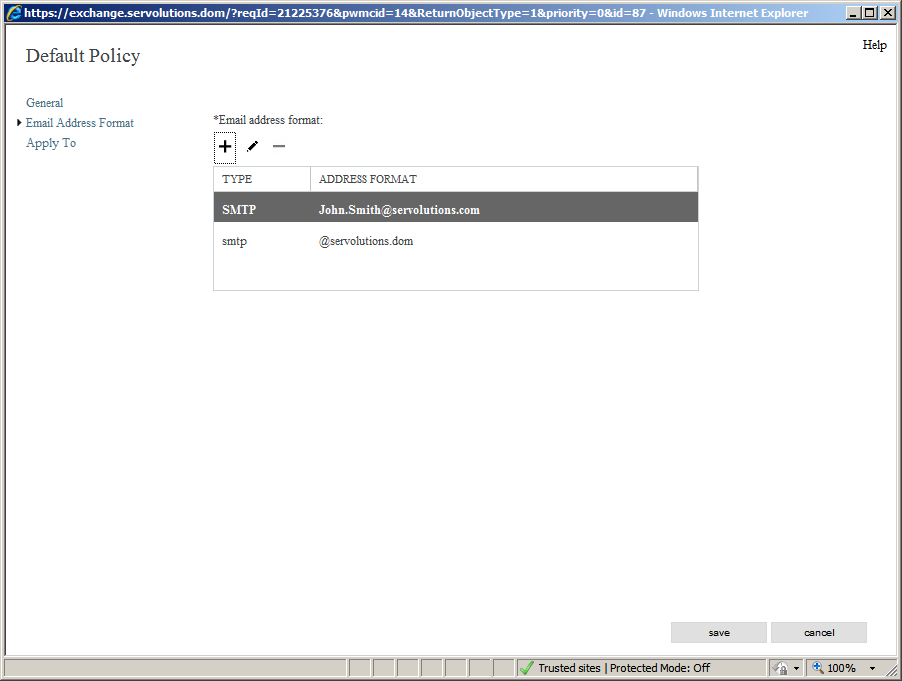
Once the changes are saved, the Default Policy window will be updated.
And that's really all. Now the server is correctly set up to send email out to the internet, receive internet from the internet (via POPcon - see below) and we have given users appropriate email addresses.
5. Installing and configuring POPcon or POPcon PRO
After going through the above 4 steps your Exchange is configured to send out email but it still can't pull down email from POP3 or IMAP mailboxes on your provider server. For this you need to install and configure POPcon.
Configuring POPcon is quite straightforward. You need to follow these steps:
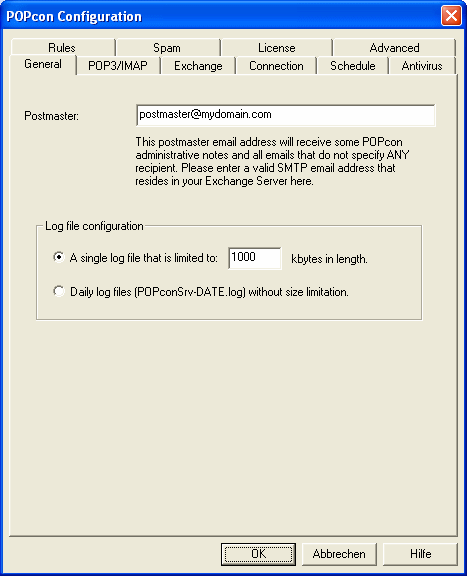
a) Configure a Postmaster email address on the GENERAL configuration tab.
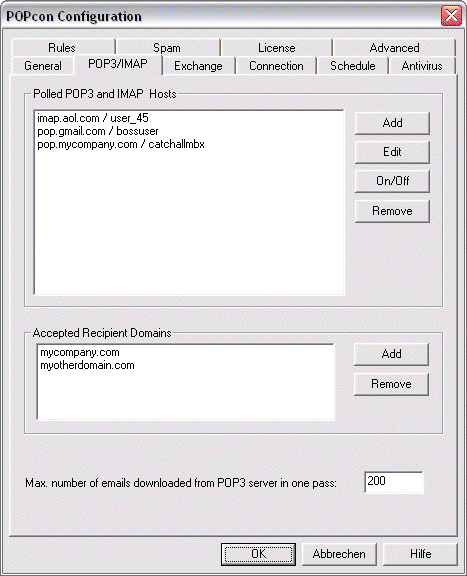
b) Add one or more POP3 mailboxes on the POP3/IMAP tab.
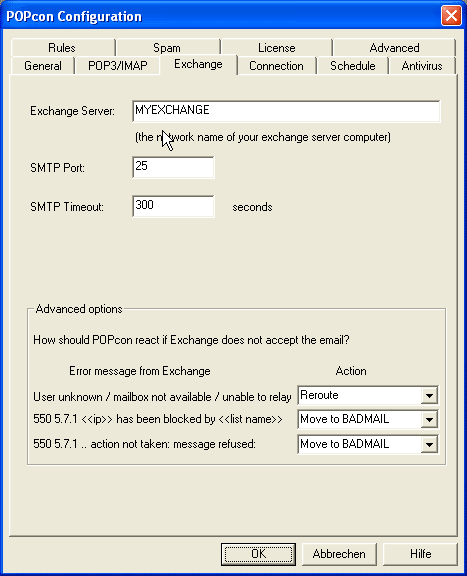
c) Configure the Exchange server name on the EXCHANGE configuration tab.
Download and run the self-extracting installer of POPcon or POPcon PRO and follow the instructions during the installation. It will install the POPcon Administrator program and the POPcon service that runs in the background on your system.
Run POPcon Adminstrator from Start > Programs > POPcon
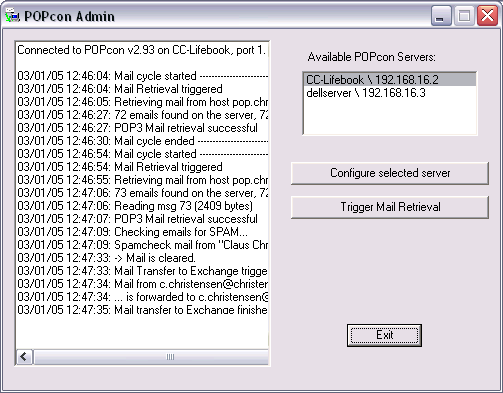
POPcon Screenshot
Click on "Configure" to open up the POPcon configuration screen.
a) Configure a Postmaster email address on the GENERAL configuration tab.
On this first configuration page you only need to enter the email address of your Postmaster or Administrator user. The Postmaster will receive all emails without a valid recipient as well as general POPcon status notifications. It is very important to define a real email address from inside your exchange server here because mails can be lost irretrievably if POPcon forwards some mail with no recipient information to the postmaster and that account does not exist in your exchange server.
You can leave the log file options to their default settings for now.
Next go to the POP3/IMAP tab to configure the POP3 or IMAP mailbox accoutns you want POPcon to download email from.
b) Add one or more POP3 mailboxes on the POP3/IMAP tab.
POPcon PRO collects mail from as many POP3 accounts you like. Just click on Add to add another POP3 host or account to the list of Polled POP3 Hosts. For each server or account you need to fill in the POP3 server settings as shown below.
If you are using catch-all style mailboxes (mailboxes that receive email for a whole domain, regardless of the recipient part before the "@") POPcon needs to filter recipients from incoming mail so only the recipients at your own internet domain are accepted. Please add the domain you consider your own in the "Accepted Recipient Domains" box. This is the same domain you configured earlier in the Exchange Default Policy.
Individual account settings
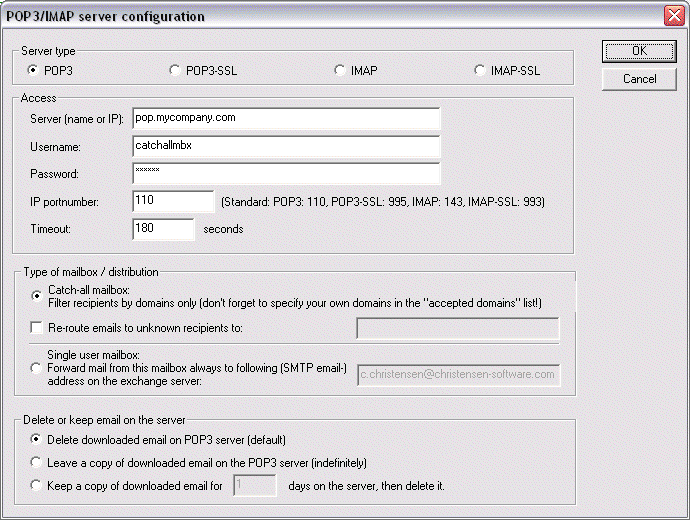
This dialog lets you input the specifics about a POP3 or an IMAP server you want to have polled by POPcon PRO.
This is the information POPcon PRO needs to know about each server:
Server type:
Here you can select on the four supported server types:
POP3: Default. POP3 servers are by far the most common mail server types on the internet.
POP3-SSL: Some POP3 Servers need SSL encryption enabled for the connection in order to protect passwords and sensitive information. Choose this type to have a SSL-encrypted connection to a POP3 server.
IMAP: IMAP Servers are also quite common and theoretically allow the client to manipulate email folders and move email between folders online. In our case the protocol is used to download email from the INBOX of the IMAP server to your exchange server.
IMAP-SSL: Supports SSL connections to IMAP servers for added protection.
Access:
Configure the server name, account name and password to connect to the mail server here.
Servername: The name the server you want to have polled. You can also enter the IP address directly.
Username: The username needed to log into your POP3 or IMAP mail server.
Password: The password needed to log into your mail server.
IP portnumber: Almost always the TCP/IP port for POP3 mail is 110. Under some circumstances, internet routers or firewalls change the port number. Please ask your network administrator or internet provider. The standard port for POP3-SSL is 995, for IMAP it is 143 and for IMAP-SSL this should be set to 993.
Timeout: Leave this to the default value.
Please ask your POP3 mailbox hosting provider if you do not have the above information.
Type of mailbox / distribution:
POPcon PRO supports both catch-all and single user mailboxes
Catch-all mailbox ("*@domainname.com"): For this type of mailbox, POPcon PRO will distribute the email retrieved from this server according to what it finds in the TO:, CC:, BCC: and other header-fields of the mail. If you choose this option, don’t forget to add your internet domain name(s) to the "Accepted Recipient Domains" box. on the POP3/IMAP configuration dialog
Single user mailbox ("user@domainname.com"): This type of mailbox receives email for only one specific Exchange mailbox. You need to specify the receiver of the email here. POPcon PRO will then direct all mail retrieved from this server to the recipient email address given here.
Delete / keep email on the server:
This block allows you to configure POPcon PRO to either delete email after downloading or keep it on your POP3 or IMAP server for a specified amount of time or indefinitely.
Delete downloaded email: This is the default setting – POPcon PRO will delete the Email on your POP3 or IMAP server after successfully downloading it.
Leave a copy of downloaded email (indefinitely): This option will cause POPcon PRO to leave a copy of the email on the server. Only use this option during testing or when you are sure the mail will be deleted eventually, i.e. by another system periodically downloading an deleting email.
Leave a copy of downloaded email for n number of days: Causes POPcon PRO to leave a copy of the email on the POP3/IMAP server for the specified number of days before deleting it. You can use this option to allow access to a single POP3 or IMAP mailbox by two different systems.
c) Configure the Exchange server name on the EXCHANGE configuration tab.
On this configuration screen you can specify the Exchange™-(SMTP) Server you want the mail to be directed to. Normally this will be the computer name of your Exchange™ server (like "MYSERVER").
You can leave all other settings default
These three steps to configure POPcon will provide you with a working set-up. Test it out by confirming the new configuration with OK and then use the "Trigger mail retrieval" button on the POPcon Administrator main screen to start the first mail download. You can follow what is happening in the scrolling log display on that screen. Watch out for any error messages there. There is also a POPcon log file (c:\program files\POPcon\POPconSrv.log – open with notepad) that you can view at your leisure.